Did You Know?
90% of the cities gas lines that get damaged are caused by not calling 811 before you dig.
This costs not only the city money to repair but creates a hazardous condition for not only the person digging but those around them as well.
know what's below call before you dig
This costs not only the city money to repair but creates a hazardous condition for not only the person digging but those around them as well.
know what's below call before you dig
Did You Know?
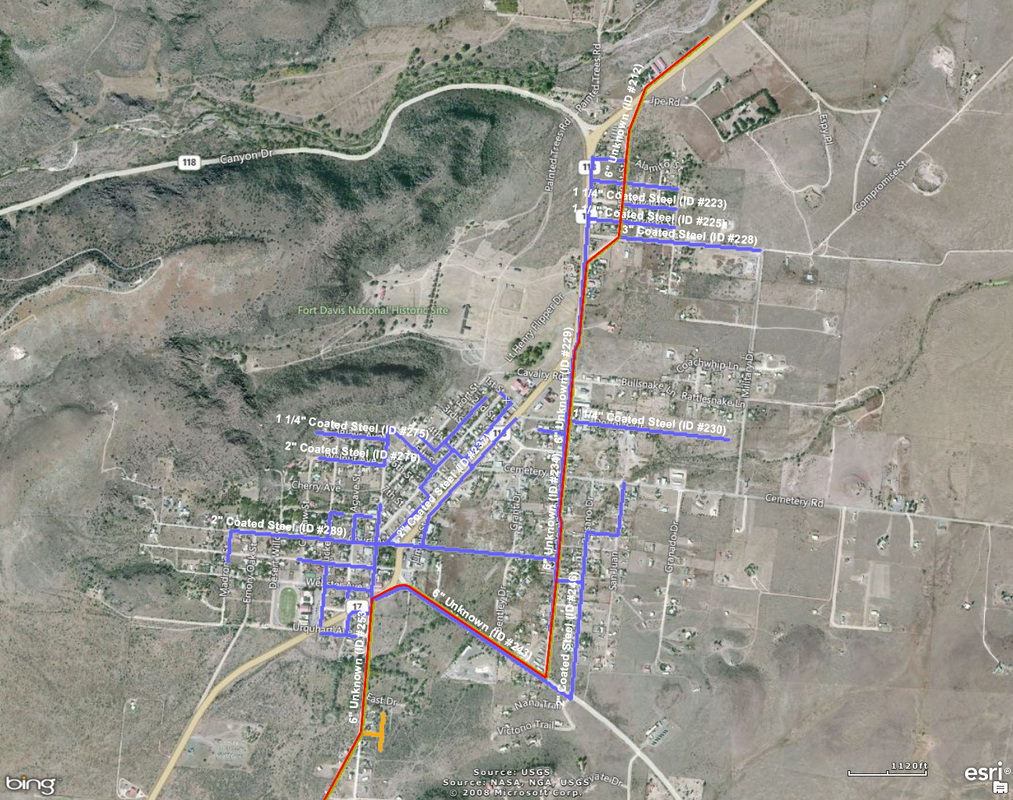
There are over 40 miles of gas main lines in the City of Alpine and over 10 miles of gas main lines in the City of Fort Davis.
This does not include the service lines that run to your houses.
Chances of hitting a gas line when digging are pretty good.
Know what's below call 811 before you dig
This does not include the service lines that run to your houses.
Chances of hitting a gas line when digging are pretty good.
Know what's below call 811 before you dig
Did You know?
Did you know?
Because natural gas is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, mercaptan (a chemical that smells like sulfur) is added before distribution, to give it a distinct unpleasant odor (it smells like rotten eggs). This added smell serves as a safety device by allowing it to be detected in the atmosphere, in cases where leaks occur
Did you know?
Natural Gas Is a Major Energy Source for the United States?
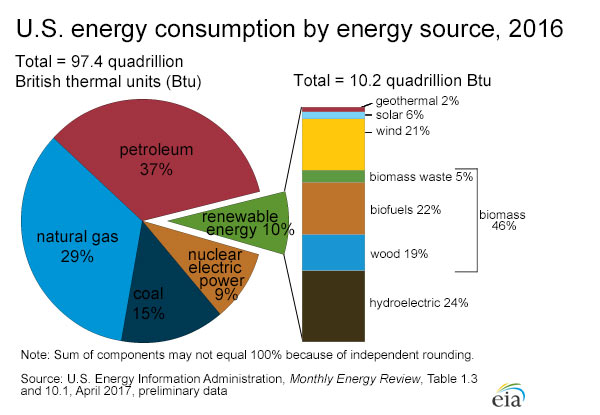
The United States used about 27.5 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of natural gas in 2015, the equivalent of 28.3 quadrillion British thermal units (Btu) and 29% of total U.S. energy consumption.
How natural gas is usedMost U.S. natural gas is used to heat buildings and to generate electricity, but some consuming sectors have other uses for natural gas.
The electric power sector uses natural gas to generate electricity. In 2015, natural gas was the source of about 26% of U.S. electric power sector energy consumption. (Other consuming sectors also use natural gas to generate electricity.)
The industrial sector uses natural gas as a fuel for process heating and for combined heat and power systems and as a raw material (feedstock) to produce chemicals, fertilizer, and hydrogen. In 2015, natural gas was the source of about 30% of U.S. industrial sector energy consumption.
The residential sector uses natural gas to heat buildings and water, to cook, and to dry clothes. About half of the homes in the United States use natural gas for these purposes. In 2015, natural gas was the source of about 23% of U.S. residential sector energy consumption.
The commercial sector uses natural gas to heat buildings and water, to operate refrigeration and cooling equipment, to cook, to dry clothes, and to provide outdoor lighting. Some consumers in the commercial sector also use natural gas as a fuel in combined heat and power systems. In 2015, natural gas was the source of about 18% of U.S. commercial sector energy consumption.
The transportation sector uses natural gas as a fuel to operate compressors that move natural gas through pipelines. A relatively small amount of natural gas is used as vehicle fuel in the form of compressed natural gas and liquefied natural gas. Nearly all vehicles that use natural gas as a fuel are in government and private vehicle fleets. In 2015, natural gas was the source of about 3% of U.S. transportation sector energy consumption, of which 97% was for natural gas pipeline and distribution operations.
Source: https://www.eia.gov
The United States used about 27.5 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of natural gas in 2015, the equivalent of 28.3 quadrillion British thermal units (Btu) and 29% of total U.S. energy consumption.
How natural gas is usedMost U.S. natural gas is used to heat buildings and to generate electricity, but some consuming sectors have other uses for natural gas.
The electric power sector uses natural gas to generate electricity. In 2015, natural gas was the source of about 26% of U.S. electric power sector energy consumption. (Other consuming sectors also use natural gas to generate electricity.)
The industrial sector uses natural gas as a fuel for process heating and for combined heat and power systems and as a raw material (feedstock) to produce chemicals, fertilizer, and hydrogen. In 2015, natural gas was the source of about 30% of U.S. industrial sector energy consumption.
The residential sector uses natural gas to heat buildings and water, to cook, and to dry clothes. About half of the homes in the United States use natural gas for these purposes. In 2015, natural gas was the source of about 23% of U.S. residential sector energy consumption.
The commercial sector uses natural gas to heat buildings and water, to operate refrigeration and cooling equipment, to cook, to dry clothes, and to provide outdoor lighting. Some consumers in the commercial sector also use natural gas as a fuel in combined heat and power systems. In 2015, natural gas was the source of about 18% of U.S. commercial sector energy consumption.
The transportation sector uses natural gas as a fuel to operate compressors that move natural gas through pipelines. A relatively small amount of natural gas is used as vehicle fuel in the form of compressed natural gas and liquefied natural gas. Nearly all vehicles that use natural gas as a fuel are in government and private vehicle fleets. In 2015, natural gas was the source of about 3% of U.S. transportation sector energy consumption, of which 97% was for natural gas pipeline and distribution operations.
Source: https://www.eia.gov